The gastrointestinal tract is a long tube where digestion takes place. From its startpoint at the mouth to where waste material such as feces is expelled from the body through the rectum, all occurs through this digestive process.
Anal canal refers to the lower portion of rectum. There are various health conditions linked to this area.
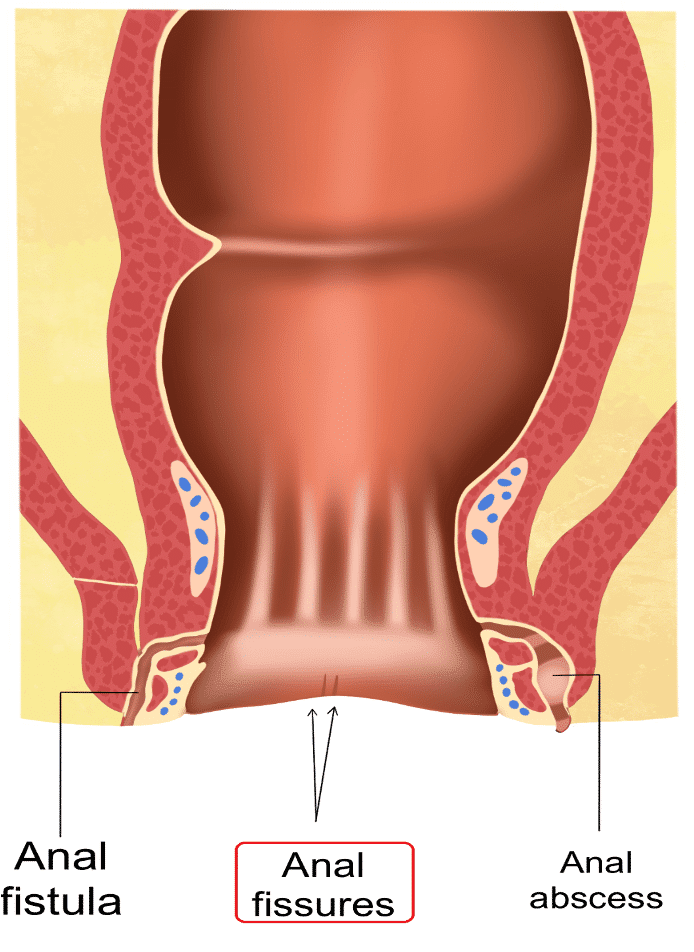
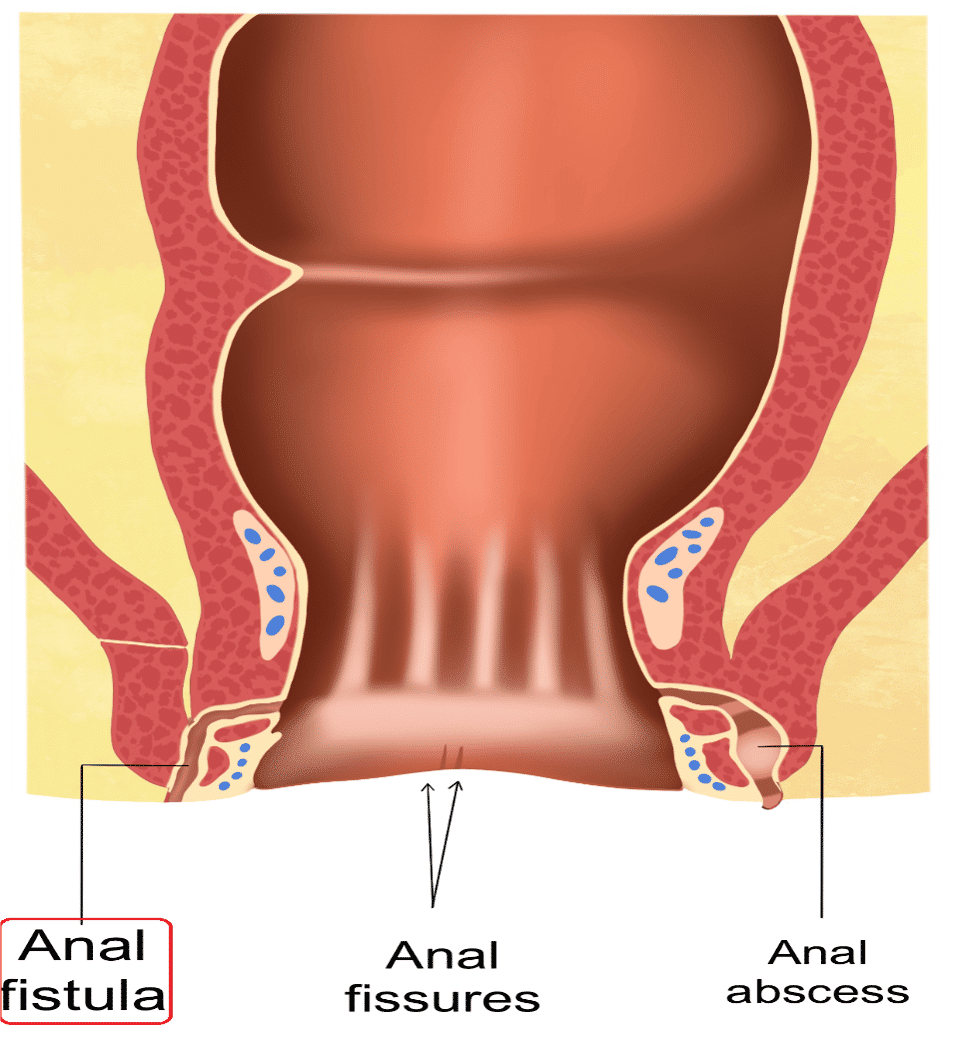
Hemorrhoids are among the most prevalent issue affecting the anal region, but there may also be conditions such as fissures, abscesses and fistulas affecting this area.
An anal fissure is a small tear in the anal canal's lining, typically caused by straining too hard during constipation. Diarrhea or infection of the anal canal may also result in such fissures, making bowel movements quite painful. Bleeding and itching may also be associated with these conditions.
DIAGNOSIS OF ANAL FISSURE
To diagnose an anal fissure, a physician will conduct an in-depth exam of the anal region. Fissures can either be acute (new) or chronic (lasting for eight weeks or more), appearing either at the front or back of the anal canal due to physical trauma or due to conditions like Crohn's disease.
TREATMENT FOR ANAL FISSURE
Treatment for anal fissures typically entails application of a specially formulated cream along with stool softeners to ease discomfort during bowel movements. The medication helps to enhance blood flow to speed the healing process. It is also recommended to keep the area clean and dry, applying talcum powder or taking warm baths all provide comforting relief. Surgery is also indicated in certain cases.
ANAL ABSCESS
An anal abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection, typically as a result of Crohn's disease or conditions that weaken the immune system. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, tenderness, fever and fatigue. Surgery and antibiotics can also be used for treatment.
ANAL FISTULA
An anal fistula is a small channel connecting the rectum with skin around the anus, often due to Crohn's disease or birth injuries. Fistulas can become infected, leading to pus drainage and irritation of surrounding skin. Diagnosis requires physical examination as well as additional tests such as colonoscopy. Treatment depends on the cause, but there are a variety of therapeutic options available for Crohn’s disease.
Anal fissures, abscesses and fistulas can all cause significant pain in the anal region. If you are concerned about any of these ailments, reach out to Digestive & Liver Health Specialists for an evaluation.
REFERENCES
1.Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2017.
2.Patkova B, Wester T. Anal Fissure in Children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2020 Oct;30(5):391–4.
3.Newman M, Collie M. Anal fissure: diagnosis, management, and referral in primary care. Br J Gen Pract. 2019 Aug;69(685):409–10.
4.Fathallah N, Spindler L, Zeitoun J-D, De Parades V. [Anal fissure]. Rev Prat. 2019 Nov;69(9):1005–10.
5.Yang J, Wang H-P, Zhou L, Xu C-F. Effect of dietary fiber on constipation: a meta analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Dec 28;18(48):7378–83.
6.Ommer A, Herold A, Berg E, Fürst A, Sailer M, Schiedeck T. German S3 guideline: anal abscess. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012 Jun;27(6):831–7.
7.Pigot F. Treatment of anal fistula and abscess. J Visc Surg. 2015 Apr;152(2 Suppl):S23-29.